What is an On-grid Solar System and How it Works?
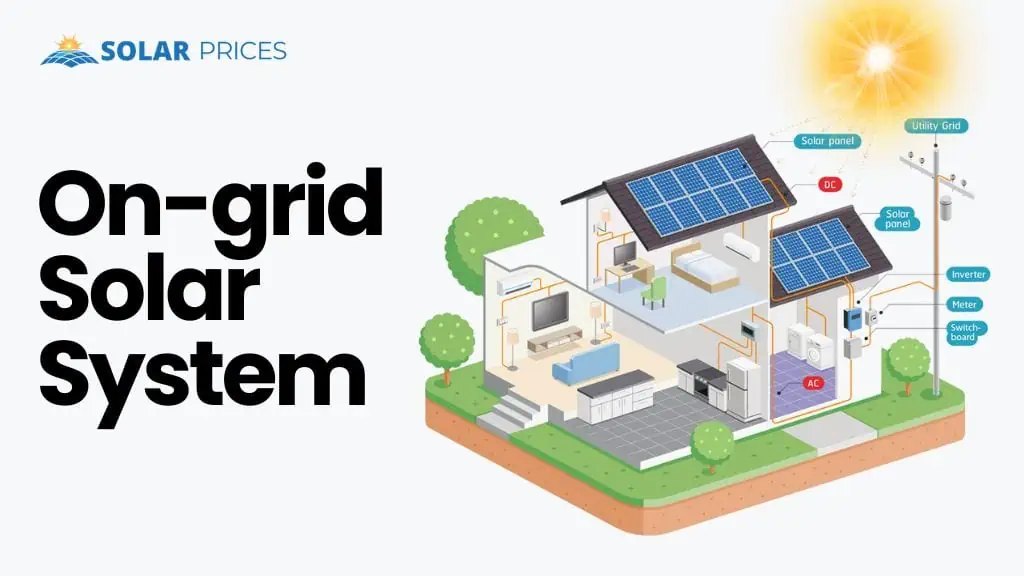
A grid-tie or an on-grid solar system is simply a solar system connected to the grid station. It uses electricity from both the solar system and the electrical grid to power the electrical appliances. Therefore, a grid-tied solar system doesn’t have to fulfill all of the electricity demands of a home or industry with solar power production.
As per the quote, necessity is the mother of invention, the solar cell was made by the Bell Corporation, later, other manufacturers have been in a race and competed with each other to dominate the solar market globally. Chinese companies have been leading the industry since then.
In this article, we will learn about an on-grid solar system and how this system works to provide electricity to power our homes or industries.
What is an On-grid or Grid-tied Solar System?
A grid-tied solar system is a system that connects its electrical production directly to the utility’s grid station. This solar system was designed to operate along with grid electricity, eliminating the need for expensive solar batteries to store electrical energy. In this way, an on-grid solar solution is more dependable and cost-effective.
Because of its grid connection, this system is referred to as a grid-tie or on-grid system. However, there is a problem with the on-grid solar system. It must be connected to a grid station, otherwise, it doesn’t work for us. But do not worry. This problem can be overcome by adding batteries to your on-grid solar system.
This backup provides energy during load shedding or power outages. Adding solar batteries to the grid-tie system increases its resilience, efficiency, and adaptability.
Aptly, this solar solution is also appropriate for people who do not want to add batteries as a backup and intend to use grid electricity when solar panels are not producing energy, particularly at night.
How Does an On-grid Solar System Work?
An on-grid solar system feeds (sends) its generated electrical power to a grid station and draws electricity from the grid. However, it is crucial to realize that an on-grid solar system alone may not be sufficient to meet your energy needs by capturing solar energy from the sun.
This is because, during times when sunshine is limited, such as at night, you will have to rely on grid electricity to meet your energy consumption.
On-grid solar systems are a popular choice among Pakistani homeowners and businesses because of their low cost. They will save you thousands of rupees on your monthly electricity costs. The system runs in several phases. Let’s go through it quickly:
- Solar panels are installed on your roof or in another sunny location.
- The solar panels convert sunlight to electrical power.
- An inverter transforms direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC).
- AC electricity is necessary to power your residence or business.
- If the solar panels produce more electricity than you consume, the excess is returned to the grid. To do so, you must have the net meter placed at your home or business location.
- If you use more electricity than your solar panels generate, the grid will provide the difference.
Benefits of using an On-Grid Solar System
Potentially, on-grid solar system has several benefits for domestic or industrial solar projects. The list of advantages include:
- It is a cost-effective energy solution that works without expensive solar batteries
- Reduce electrical dependence and save a lot of money on electricity bills
- Reduce carbon footprint and help restore the environment.
- A seamless and dependenable energy resource
- Increase your property value (home’s value)
Components of an On-grid Solar System
The grid-tie or on-grid solar system works by connecting its solar production to a grid station. This condition makes it impractical for a remotely situated region or area.
However, other electrical solutions such as an off-grid solar system serve best for remote places with no grid connection or national electricity solutions available. An on-grid solar system comprises of the following components:
- Solar Panels
- Grid-tie inverters
- Net Meter facility approved
- Connection to the utility grid
- DC switches
- Charge controller
- AC & DC wires
- AC & DC breakers
- AC & DC connectors
- DC connection BOX
- Change over devices
- Tubular / Lithium Batteries (optional)
An on-grid solar energy production can be divided into some bullet points as given below:
- Electrical energy generation
- Energy conversion
- Electricity supply
- Electricity storage
- Net metering integration
Electricity Generation: The electricity is generated using solar panels made of silicon wafers. The silicon atoms have loosely bound valence electrons. When solar panels are exposed to solar energy (sunlight), the energy in the solar radiation is delivered to the electrons, which become excited upon absorbing all of this energy.
The energized electrons become free and begin traveling in a circuit. The motion of free electrons results in the generation of an electrical current.
This electrical current, through the wires, is then directed to the solar inverter for further operations. These wires are excellent conductors exhibiting little electric resistance, resulting in no energy loss throughout the transmission of electrical energy from generation to end usage.
Energy Conversion: solar panels (Photovoltaic cells) produce Direct Current or DC electricity. This is then delivered to the inverter via connecting wires. This direct cannot be used by the AC home appliances on the premises because all electrical appliances require alternating currents.
These devices run on specific voltage ranges to function optimally. So, the inverter is responsible for converting the produced energy into usable power.
The latest grid-tie inverters are the most efficient and ensure that there is the least current loss. The on-grid solar inverter employs a transformer-type operation to convert the current to an alternating current with an average voltage of 240 volts.
The inverter regulates all of the input and output features of the system to ensure that it functions properly, as a result, the inverter is known as the “brain” of the solar system.
Energy Supply: As mentioned earlier solar panels generate a direct current (DC), and an inverter converts this electricity into a 240-volt AC supply. This powers the home appliances via highly conductive cables. The electrical wiring should lose little to no electrical energy during its transfer.
Electricity is supplied based on the appliances utilized on the property. The more appliances used, the more electricity is delivered to the house while less is stored. When the electricity consumption exceeds the supply, the grid station provides additional electrical power.
Electricity Storage: The surplus electricity generated by the solar system throughout the day must be stored somewhere, otherwise it will go to waste. To address the issue, these solar systems utilize grid stations as virtual batteries.
This facility makes the solar-based electrical system more affordable than a battery-based solar system (off-grid solar system). The grid station receives all of the electricity generated by the on-grid solar system that is not being consumed by the associated devices.
Net Metering Process: Net metering is an electrical billing mechanism that lets consumers feed their power production to the grid station and use it at the time they need.
Each country has its own set of rules for buying electricity via net metering. This facility in Pakistan works differently than others. Pakistan uses net metering to assess power provided to grid stations during off-peak hours.
Owners receive credits for electricity units, which are applied to their account, and the final amount after deducting grid charges. This enables users to optimize their investments.
Is Grid-Tie Solar System In Pakistan Worth it?

It is worth its cost. It is the most widely installed solar system in residential, industrial, and commercial solar projects across Pakistan. A grid-tied solar system connects to the electrical grid station and utilizes power from both the installed solar panel system and the electric grid station. As a result, a grid-tied solar system does not need to supply the entire home’s electrical usage.
These are economical and effective solar solutions, and many homeowners utilize them because of their low cost and net metering options. Industrial customers prefer this system since it does not require batteries, which are quite expensive for industrial machines. Adding batteries to a grid-connected system also provides backup power during outages.
The Bottom line
The on-grid solar system offers an excellent choice for saving money on bills. This is a cost-effective solar system that needs no batteries for backup power. Additionally, renewable energy helps reduce your carbon footprint and boost the value of your home. Such systems provide continuous access to electricity unless the grid goes down.
Many users aim to cover 100% or nearly 100% of their energy usage with on-grid solar systems. They can achieve this target by selling excess energy produced during the day to the national grid system. Electrical energy sent back to the grid will be compensated through net metering in many places (cities) in Pakistan.
Net metering credits your account for electricity sent to the grid, offsetting charges when drawing from the grid later. During grid outages, unless opting for a grid-tied system with battery backup, the electricity supply is cut off. Solar panels produce the cheapest electricity in the world. Switch to solar energy, look for a trusted solar company or installer, and start saving thousands of rupees every month.