How Solar Panel Works? | A Comprehensive Review on Solar Panel Working
Solar panels generate electricity directly from the sunlight. We can use that electricity to power our homes, factories, or other business properties. Talking simply, there are numerous solar panel applications ranging from rooftops to heavy spacecraft or satellites.
The central focus is always to generate sustainable energy to power our electrical and electronic appliances. So, the question here arises how does a solar panel work or what is the working of solar panels? Or someone can ask how solar panels convert solar energy into electricity.
In this article, I will explain the basics of how solar panel works, frequently asked questions about solar panels, solar panel working principles, and more!
Click here to learn the latest solar panel price updates!
Basics of Solar Panel Working
Solar panels help to reduce carbon emissions and hence compensate the global warming. It’s simple to comprehend how solar energy is a clean, green, and sustainable electricity resource.
You might be familiar with PV (the photovoltaics or photovoltaic effect). Learning how it helps solar panels convert sunlight into electrical energy is very straightforward.
What is Photovoltaics or Photovoltaic effect?
The photovoltaic effect is the foundation of all the chemical and physical mechanisms behind the latest solar cell technologies. Edmond Becquerel, in 1839, was the first person to observe and report the photovoltaic effect.
Statement
“The electric current is produced when a semiconducting material like silicon or germanium is exposed to sunlight. This phenomenon is known as the photovoltaic effect or photovoltaics.”
How do solar panels generate electricity for your home? Step-by-step explanation
Producing electric current is the final result (output) in working solar panels, but the process is a bit technical. First the basics:
A solar panel is a whole entity (a solar module) but the main part of it (essence) is the photovoltaic cell inside the panel that converts the sunlight into electricity. Today, more than 95% of solar cells are made using crystalline silicon (c-Si) and it is the second most abundant element on Earth.
Solar cells consist of a photoactive layer around 160–170 μm in thickness. Pure silicon itself is unable to efficiently produce electricity but the impure semiconducting material does. So, extrinsic silicon is produced by doping the phosphorus and boron impurity atoms in pure silicon.
These two elements (phosphorus and boron) are used as positive and negative doping agents in the solar cell industry. They help to develop the positive and negative layers of a solar cell.
Here’s how solar panels produce electricity from sunshine:
Solar cells absorb the sunlight and convert it to direct current. This current is either stored in batteries or used to run electrical loads. If the electrical appliances work on alternating current, we have to use a solar inverter in our solar system.
Solar inverter mainly functions to convert DC input power to AC output power. These days, solar inverters are much more advanced and perform important functions.
This is how a solar panel works in a house to generate electricity. A solar inverter does the job of transferring alternating current to energy to your electrical appliances at home.
Till now, you are almost done. What’s next to know about solar panels working? Let’s learn in more simple or layman’s language how solar panels produce electrical power for us.
How does a solar panel work to produce electricity?
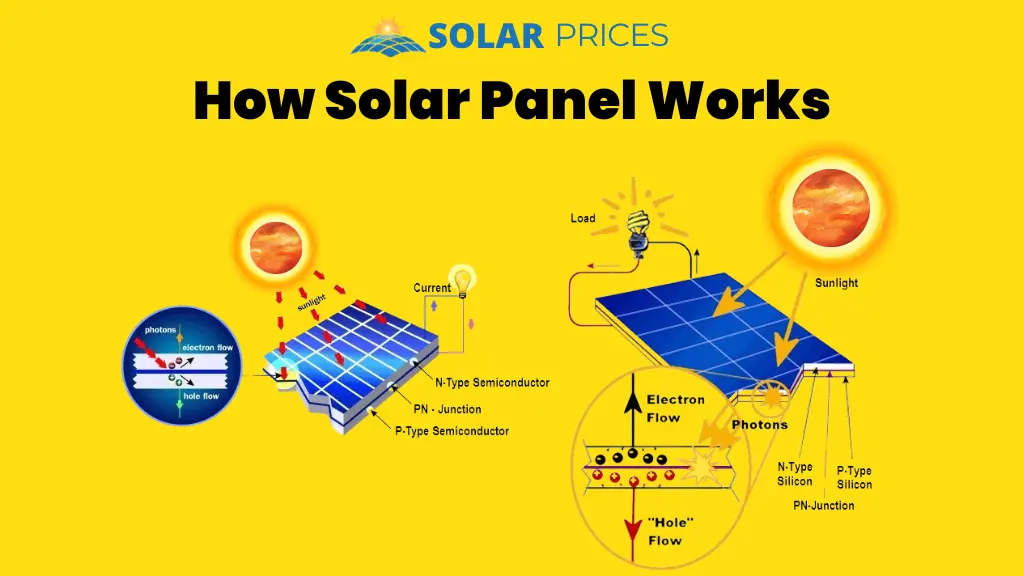
A solar panel or solar module comprises many solar cells that convert solar energy into electricity. The photovoltaic effect is the key component in it, as discussed earlier. Photo means light or photons of light energy.
When the sun shines onto a solar panel, the photon energy from the sunlight is absorbed by extrinsic silicon layers in the solar panels. This photon energy liberates free electrons throughout the silicon structure, creating electron-hole pairs and an internal electric field.
The charges move in response to an internal electrical field in the cell, causing electricity to flow. This is all that goes into learning how solar panels work on the rooftops or solar farms.
How Solar Panel Works? Insights of Chemistry and Physics Involved?
If you are a student of science and interested in learning how solar panel works or investigating solar panels working, the basic atomic concepts of chemistry and physics can help you a lot. Let’s learn the workings of solar cells below.
Solar cells are manufactured with two types of extrinsic semiconductors ( namely p-type and n-type silicon). These two types are prepared by the process of doping, adding trivalent or pentavalent atoms to the pure silicon material.
The p-type semiconductor is produced by adding atoms having 3 electrons in the valance shell (atoms like gallium or boron). Such atoms are one electron deficient in the outer energy level as compared to the silicon atom.
Because boron has free space for an electron, an electron from the surrounding silicon atom is snatched (accepted) by the boron nucleus, and an electron-hole or vacancy is produced.
Following the same procedure, the n-type semiconductor is prepared by adding atoms that have 5 electrons, such as phosphorus, in the valance shell, containing one extra electron in the valance shell than the silicon atom.
There are 5 valance electrons in the outer energy level of phosphorus, one more electron than silicon. So, phosphorus makes 4 single bonds with its neighboring silicon atoms, but one electron out of five is set free to move inside the silicon structure and not bonded to any atom.
A solar cell is made with different layers of semiconducting materials of both n-type and p-type. These layers are arranged in a way that p-type silicon is present in front of an n-type silicon layer.
In the n-type extrinsic semiconductor layer, electrons are in excess, and the opposite happens with the p-type semiconducting layer, positively charged holes are the majority carriers (electronic vacancies) there.
When these layers are brought into direct contact, a junction becomes between the two layers. The electrons, the majority carriers in n-type, cross the junction and rhea the other side of the junction to fill the vacancy in p-type material.
This move of the free electrons from the n-type layer produces a region around the junction, known as the depletion region or zone.
Schematic representation of a solar cell, showing the n-type and p-type layers, with a close-up view of the depletion zone around the junction between the n-type and p-type layers.
The p-type side of the depletion zone, where holes were previously present, now contains negatively charged ions, and the n-type side, where electrons were present, now contains positively charged ions, once all of the holes in the depletion zone have been filled with electrons.
Because of the internal electric field produced by these oppositely charged ions, holes in the p-type layer cannot be filled by electrons from the n-type layer.
The bottom line of the whole story, when a solar cell is exposed to sunlight, photons of energy are absorbed, and hence electrons in the extrinsic silicon material get free to move all around in the structure, so, it leads to the formation of “holes”.
The presence of an electric field will transfer electrons to the n-type layer and holes to the p-type layer. Hence electrons will flow from the n-type layer to the p-type layer by crossing the depletion region.
These electrons then pass through the external wire and reach the n-type layer if we connect both (n-type and p-type) layers through a conducting wire.
In the following section, the typical questions about solar panels are answered one after the other in a summarized and simple way. Let’s get straight into it.
Frequently asked questions related to solar panels
The whole world is shifting towards solar energy because solar energy can save us a lot of money on electricity bills, help to protect our environment, and also generate electrical energy backup for nighttime and blackouts. So, the services of solar panels are highly promising for humanity and the Earth.
There is a long list of questions related to working and other aspects of solar panels. To make it clear and simple, preciseness is important. With a detailed discussion about the working of solar panels above, you get to know how solar panels produce electricity and all the science behind it. Check out the most frequently asked questions by homeowners in the following.
Do solar panels need a hot climate to work?
No, this is not required by the solar panels. Some people think that solar panels have the potential to generate more electricity in the summer.
It seems true but the reality is a bit different. The stronger sunshine and warmer climate suit the solar cell production mechanism and hence in summer there is a chance of higher production. On the real ground, if the temperature gets much hotter or colder, solar panels become less efficient.
How do solar panels work on a house?
After all the basic calculations of electrical load, a suitable solar system is designed to meet the electrical needs of that house. Required solar panels, south-facing, are installed on the rooftop. These solar panels when exposed to sunlight, they convert solar energy into electricity.
Do solar panels work at night?

Traditional crystalline silicon solar panels do not work at night. If your solar system includes a battery backup or battery storage option, you can use that energy at night time.
Can you run your whole house on solar power?
Yes, you can, but it depends on the solar system size and your electrical load. Although a solar system can produce enough energy for your use in the daytime, it is not sure that every day the weather will be clear and the sun will shine strong. Planning considerable battery storage will help if want to be independent of your local grid power station.
Do you still have an electric bill with solar panels?
Yes, no matter if you have installed solar panels, you have to pay electricity bills unless you cut your grid supply or stop using the Wapada supply.
If you want to stop your grid supply or to become energy independent, you will have to include solar battery backup into your solar system.
Do solar panels work on cloudy days?
Solar panels absorb the visible light from the sun. Simply said, if there is enough light to walk, there is enough light for solar panels to produce electricity. However, the stronger the sunshine, the more power solar power production.
