How to Apply for Net Metering in Pakistan? Green Meter Application

Green Meter Application
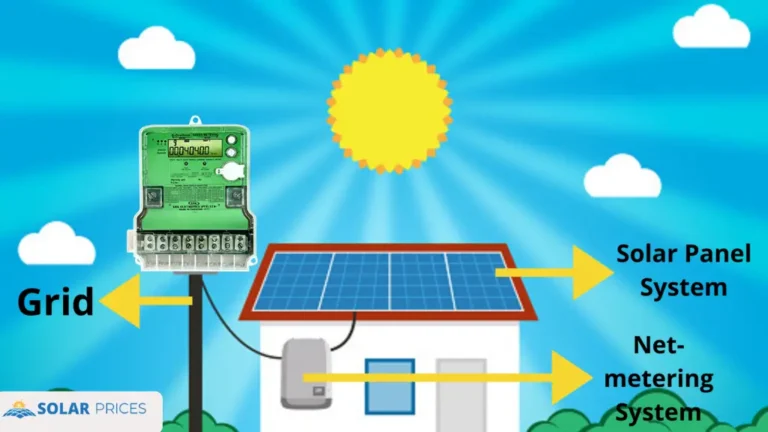
Net metering (green meter installation) is a fantastic project launched by NEPRA in 2015 that allows homeowners and businessmen to easily export any surplus electricity to national grid and earn credits. Whenever a solar system generates extra electricity than they consumes, the excess energy is transported to the national grid.
NEPRA has defined a comprehensive application process for net metering in Pakistan. Let’s learn each step of the net metering application procedure in Pakistan, one by one.
If you’re planning for net metering of your solar system, first consult with a reputable solar supplier or solar company near you. The company will facilitate the net metering application process seamlessly. Check out the things below you have to do before net metering initialization:
- Solar System Installation: Before applying for a net metering system in Pakistan, you must have a solar PV system installed at your residence. The solar system must be either on-grid or hybrid, with a three-phase meter connection. After all, without a solar PV system, there would be no way to export energy to the national grid. As a result, to benefit from Pakistan’s net metering provision, you must have solar panels placed on your roof.
- Connect with an AEDB Registered Solar Company: The first thing you should do if you already have a solar system is get in touch with a local AEDB-registered solar provider. Why is it that you cannot apply for net metering on your own, one may ask. The reason is that individual applications for net metering are not permitted by NEPRA. Rather, you need to work with a solar firm that is approved to manage the application procedure for net metering. Speak with the solar firm and give them the go-ahead to submit the Pakistani net metering application.
- Preparation of Application: Your net metering application procedure starts the moment you get in touch with an AEDB-registered solar provider, like Alpha Solar. At this point, the business will ask to see your electricity bill and National ID card, among other important documents. They will send it to the appropriate department and offer thorough assistance at every stage of the application procedure.
- Inspection and NOC Issuance: Once the application is granted approval,. It proceeds to the following step, where the Punjab Energy Department conducts an inspection and issues a No Objection Certificate (NOC) in accordance with SRO 892 (1)/2015. This stage guarantees that all rules and standards are followed and upheld.
- Signing of Agreement: Following the issuing of a No Objection Certificate, a contract is signed between the consumer and the local electricity provider, such as LESCO. The agreement is valid for three years, during which you may export excess electricity generated by your solar panels to the national grid.
- Allotment of Generation License: Once signed, the agreement is forwarded to NEPRA (National Electric Power Regulatory Authority) for certification. This critical stage assures compliance with legislation and gets you the official generation license. This license authorizes you to operate as an independent power producer for a period of three years. With this license, you have legal recognition and permission to contribute to the national energy system through solar power generation.
- Activation of Net Metering: When you successfully receive the generation license, your net metering services will start. You will have a net meter placed at home and will be able to save money by selling electricity to the grid.
- Reputed Solar Resources to Support: A reputable solar company near you can assist you with everything from “solar system installation” to “NOC issuance” and “net metering activation,” relieving you of the stress of having to complete all of the stages. Simply contact that firm and have their pros handle your net metering system with experience and efficiency.
How does Net Metering in Pakistan Work?
The most basic kind of net metering is the one mentioned above; it’s also known as “true net metering” or “1-for-1 net metering” because the utility credits customers for every kWh of electricity they send into the grid, which can then be applied to kWh used during off-peak hours.
When a homeowner installs a solar energy system, the utility replaces the electric meter with a new bi-directional meter.
This new meter can record both the energy that the customer uses from the grid when the solar panels aren’t producing enough power to run the appliances in the house and the energy that the solar panels export to the grid.
The utility computes the total amount of energy used from the grid and sends it to it after each billing month. The utility company bills the homeowner for any excess electricity they use over what they supply.
If they send more than they consume, the utility records a credit balance, which is then applied to the following month’s account.
The functioning of all net metering programs has variations among them. The key differences among different net metering programs include:
- Credit rollover (monthly vs. annual vs. indefinite)
- Value of credits
- Time of use rates
Net Metering Credit Rollover
The majority of net metering programs allow kWh credits to roll over from month to month, so energy credits earned during the sunny summer months can be applied to consumer expenditures of energy during the colder winter months.
While some utilities let these credits roll over indefinitely, the majority reconcile any credits that are left over at the end of a year and provide the consumer a near-wholesale rate in return.
The date that a customer’s solar panels were granted permission to operate (PTO) and connected to the grid is known as the “true-up date,” and it is often established on that basis.
While some utilities let solar customers choose when to do their yearly true-up, others have a single date that is fixed for everyone.
This date is typically in late spring to offer solar owners the best opportunity to use up any banked credits from the previous year before the new sunny season.
There are locations where monthly reconciliations of net metering credits occur as well. At the conclusion of each billing cycle, any unused energy credits are paid to the owner of the solar system, typically at a significantly discounted cost that is comparable to the wholesale price of electricity.
Because of this, net metering’s financial advantages are diminished, and homeowners in these areas may decide to build a solar power system that won’t use more energy than they need during the summer.
Value of Net Metering Credits
Every kWh credit under genuine net metering is equivalent to a kWh, and it can be exchanged for grid energy at any moment.
Instead, some net metering schemes offer a cash bill credit. Sometimes the credit is less, while other times it is exactly equal to the retail value of a kWh.
Time of Use Rates
Time of use (TOU) rate plans are available from certain utilities; under these plans, the price of energy varies based on when it is utilized.
Weekday evenings are often when the grid experiences its peak demand as most people get home from work and start using their appliances. It is at these periods that energy prices rise.
There are at least two distinct charges for on-peak and off-peak periods in TOU rate plans. Owners of solar panels that pay time-of-use (TOU) tariffs are credited for the electricity generated on their panels and sent to the grid.
Let’s take an example where a solar installation sends 10 kWh to the grid at 8 rupees per kWh during the off-peak hours. For such energy, the owner would receive an 80 rupees credit.
Only roughly 6.7 kWh of peak-time electricity might be offset by the credit they received if grid energy is valued at 12 rupees per kWh during those hours.
TOU rates might increase the financial benefit of a home solar battery due to the fluctuating value of energy. To avoid paying peak energy rates in the evening, homeowners can use the stored energy in their battery to charge it with solar energy during the day.
Explore recent developments in the solar industry: What are Night Solar Panels
Conclusion
Net metering catalyzes renewable energy adoption, empowering consumers to harness the full potential of solar energy while realizing substantial cost savings.
By following the given application process and leveraging the expertise of reputable solar providers, consumers can seamlessly process the net metering application, ensuring compliance and efficiency at every stage.
Moreover, understanding the intricacies of net metering programs enables consumers to optimize energy usage, maximize financial benefits, and contribute to a sustainable energy future.
FAQs:
What is Net Metering?
Net metering is a billing mechanism that allows solar energy system owners to export the excess electricity they generate to the grid. This helps them offset their electricity costs.
Who is eligible for net metering in Pakistan?
Individuals in Pakistan with installed solar PV systems, compliant with regulatory standards, and connected to the national grid through an AEDB-registered solar provider are eligible for net metering.
What Documents are Required for the Net Metering Application Process?
Essential documents include the electricity bill, National ID card, and other relevant certifications and permits related to the solar energy system installation.
How Does Net Metering Benefit Consumers?
Net metering enables consumers to reduce their electricity bills by selling surplus solar energy to the grid, earning credits for excess generation, and contributing to a sustainable energy future.
What Variations Exist in Net Metering Programs?
Net metering programs may differ in credit rollover policies, value of credits, and time-of-use rates, depending on local regulations and utility policies.
If you Are interested in gaming related blog’s Must visit This site :- Forfods.com